With a displacement hull there is no significant advantage in using an engine that will drive the vessel faster than nominal hull speed at 70 or 80 percent of rated RPM. Semi-displacement hulls tend to have wide flat aft sections - like a New England lobster boat.

18 Hulls Can Be Classified According To Their Hull Types Desired Download Scientific Diagram
An iconic Krogen design with a ballasted displacement hull and tremendous storage a proven cruising or liveaboard yacht.
. A displacement hull is a boat hull design that uses buoyancy to support its weight. Thats why this design is widely used on cruisers and sailboats. Semi-Displacement Hulls Semi-Displacement Hull Boats.
This type of hull is designed to push through the water moving or displacing the water in a. These hulls are designed to partially climb on top of the bow wave and separate the transom from the stern wave. The square root of a 16-foot displacement hull is four which multiplied by 134 gives a top speed of 536 knots.
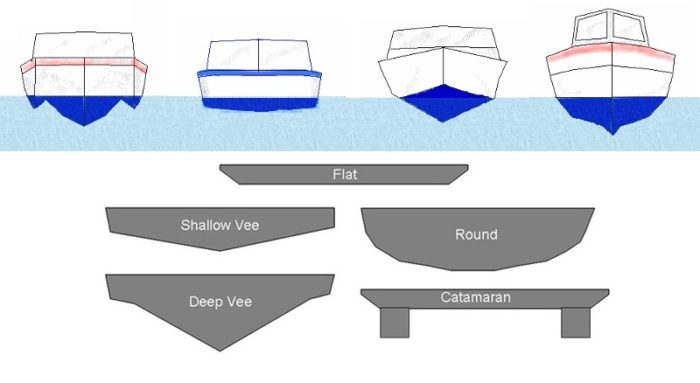
A round-bottomed hull shape acts as a displacement hull. A boat with a displacement hull may ordinarily be distinguished by a deep V shape to its bottom or hull. Its very stable in rough waters.
Semi-displacement speeds are usually in the area of 15 to 25 square-root LWL in knots. A displacement hull and a planing hull. Describing a full displacement hull is very similar.
The amount of water displaced is equal to the weight of the ship itself. Displacement Hulls That weight is the boats displacement. A large ship a tugboat a barge or a sailboat are displacement hulls.
A round-bottomed hull shape acts as a displacement hull. They behave like displacement hulls at low speed but pop up onto a plane usually around 15-16 MPH depending on the design and load. Generally displacement hulls are slow as they are not designed to naturally plan the speed at which they move through the water is limited by its waterline length.
A displacement hull and a planing hull. Shaped hull and only be displacing an amount of water equal to partial weight of the boat. The hull is solid fiberglass below the waterline and cored above.
This wasnt always so. These hulls are smooth and typically lack the chined designs of planing hulls. Boats with displacement hulls are limited to slower speeds.
A displacement hull has a belly or convex bottom contour or planing surface. Unfortunately many people tend to think that all full displacement vessels are the same. Displacement hulls are often rounded and would be termed round bottom hulls.
A round bottom provides a soft ride at the hull speed. Displacement Ships with this hull move through the water by displacing water meaning it pushes the water aside. They are designed to move with very little propulsion or force.
V-Bottom Hulls V-shaped hulls are also planing hulls. Most of these modem forms have an underwater hull shape that has a striking resemblance to faster planing hulls. Until hull 65 1985 they were built with glass-over-plywood decks.
For practical purposes rather than strictly theoretical ones it is the wave making property of the typical displacement hull that causes the rapid rise in resistance and is related to boat length the wave system set up that is parallel to the direction of travel propagates predictably according to speed in that a given speed gives a given wave length it is when the. At high speeds a displacement hulls tail will sink down lower and lower as a result of the hole created in the water as the surfboard moves forward. There are two essential types of powerboat hulls.
What hull is a displacement hull. We can differentiate between full displacement hulls based upon two form fundamentals. It takes a lot of power to drive a hull in.
Most powerboats and personal watercraft have planing hulls that ride on the water at higher speeds. Earlier in the century when huge engines werent an option long narrow semi-displacement boats were among the most prized race horses of the era. Longitudinal symmetry and displacement-to-length ratio DL.
A round bottom powerboat has little or no discontinuity in the curve of its section between the gunwale and keel. This helps them perform in anything from. Thereafter they were built with a cored deck and superstructure.
An s-shaped hull is typical of deep bottom canoes and of course sailboats having the most extremely pronounced deep keel. It lies partially submerged and displaces water when moving hence its name. A boat with a displacement hull may ordinarily be distinguished by a deep V shape to its bottom or hull.
With the same amount of horsepower applied hulls with a lower DL ratio will cruise at a faster speed than hulls with a higher DL ratio. This type of hull is designed to push through the water moving or displacing the water in a proportion equal to the weight of the boat. The amount of water it displaces is equal to its weight.
This is the oldest design for ships and boats. Most large cruisers and most sailboats have displacement hulls allowing them to travel more smoothly through the water. The Krogen 58 has a displacement hull providing stability and seaworthiness The biggest limitation these vessels have is their speed which is constrained to that of an open-ocean wave of the same length as the hull at the waterline.
The laws of physics which says that the maximum achievable speed is 134 times the square root of the waterline length govern performance of these hulls. There are two essential types of powerboat hulls. Most large cruisers and most sailboats have displacement hulls allowing them to travel more smoothly through the water.
S-Shaped Hulls S-Shaped Smooth Displacement Hull. Planing hulls come in a variety of shapes each of which has it benefits and disadvantages. Vouch Displacement Hulls are made to surf more types of waves than youre average intense hull design rails have a little more volume and the amount of belly in the nose is reduced from some others interpretations.
What type of hull is best for rough water. Boats with displacement hulls are limited to slower speeds. Nothing could be further from the truth.
Which of these hulls is a displacement hull. In basic terms it displaces the same amount of water when stationary or moving it is supported by buoyancy and they are typically big round and bulbous. There are three main categories of hulls.
Semi-Displacement Hull Local Coastal and.
Neville S Magic Hull Shape Passagemaker
Boats 101 River Runners And Creek Boats Blister
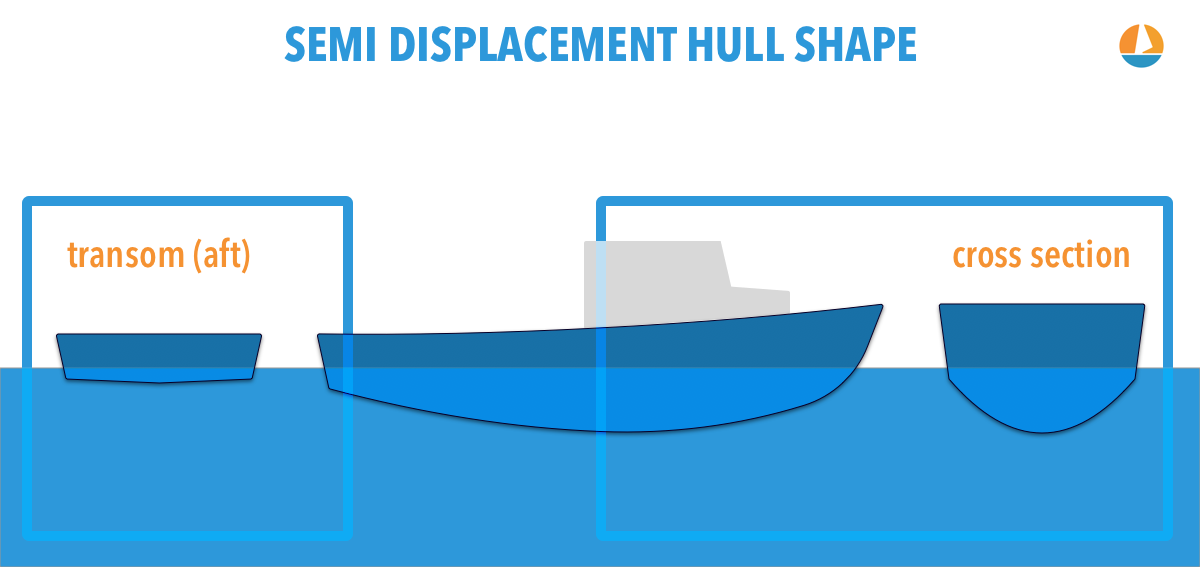
Semi Displacement Hulls Explained Illustrated Guide Improve Sailing
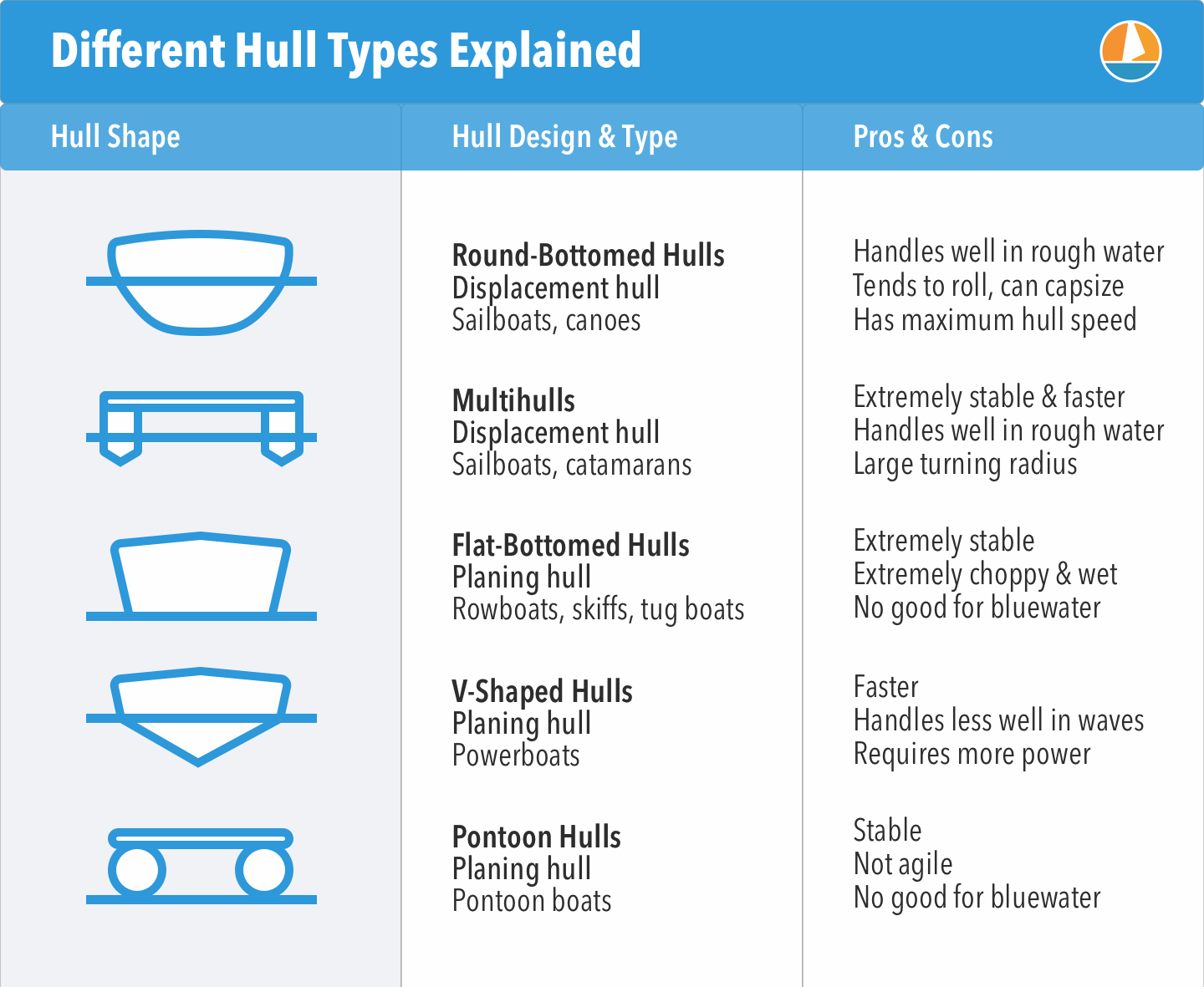
The Illustrated Guide To Boat Hull Types 11 Examples Improve Sailing

0 comments
Post a Comment